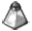
Center of the galaxy via MeerKAT, a new radio observatory in Africa.
MeerKAT radio telescope inaugurated in South Africa – reveals clearest view yet of center of the Milky Way – SKA SA
“We wanted to show the science capabilities of this new instrument”, says Fernando Camilo, chief scientist of the South African Radio Astronomy Observatory (SARAO), which built and operates MeerKAT in the semi-arid Karoo region of the Northern Cape. “The centre of the galaxy was an obvious target: unique, visually striking and full of unexplained phenomena – but also notoriously hard to image using radio telescopes”, according to Camilo. The centre of the Milky Way, 25,000 light-years away from Earth and lying behind the constellation Sagittarius (the “Teapot”), is forever enshrouded by intervening clouds of gas and dust, making it invisible from Earth using ordinary telescopes. However, infrared, X-ray, and in particular, radio wavelengths penetrate the obscuring dust and open a window into this distinctive region with its unique 4 million solar mass black hole. “Although it’s early days with MeerKAT, and a lot remains to be optimised, we decided to go for it – and were stunned by the results.”
“This image is remarkable”, says Farhad Yusef-Zadeh of Northwestern University in Evanston, Illinois, one of the world’s leading experts on the mysterious filamentary structures present near the central black hole but nowhere else in the Milky Way. These long and narrow magnetised filaments were discovered in the 1980s using the Very Large Array (VLA) radio telescope in New Mexico, but their origin has remained a mystery. “The MeerKAT image has such clarity”, continues Yusef-Zadeh, “it shows so many features never before seen, including compact sources associated with some of the filaments, that it could provide the key to cracking the code and solve this three-decade riddle”.